Code
cint <- dget("C:/Dataset/cint_data_11042021")nlmecint <- dget("C:/Dataset/cint_data_11042021")Since this is a large dataset we start off by selecting the variables we need, convert it to the long format, and generate the “Time” variable
df <-
cint %>%
select(
sid, cca_0, cca_12, sex, ageyrs, resid, physical,
hpt_old, cart) %>%
gather(period, cca, cca_0:cca_12) %>%
mutate(
Time = ifelse(
period == "cca_0", 0,
ifelse(period == "cca_12", 1, NA)))Here we begin to pick up abnormal or suspicious data escpecially in the cca. One way is to determine the changes with time
df2 <-
df %>%
arrange(sid, period) %>%
group_by(sid) %>%
mutate(
cca_prev = lag(cca, order_by = sid),
cca_diff = cca - cca_prev)
df2 %>%
arrange(sid, period) %>%
head(10) %>%
kableExtra::kable()| sid | sex | ageyrs | resid | physical | hpt_old | cart | period | cca | Time | cca_prev | cca_diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 58 | Urban | Yes | No | Naive | cca_0 | 0.925 | 0 | NA | NA |
| 1 | Female | 58 | Urban | Yes | No | Naive | cca_12 | 1.000 | 1 | 0.925 | 0.075 |
| 2 | Female | 48 | Urban | Yes | No | Naive | cca_0 | 0.975 | 0 | NA | NA |
| 2 | Female | 48 | Urban | Yes | No | Naive | cca_12 | 0.700 | 1 | 0.975 | -0.275 |
| 3 | Female | 40 | Urban | Yes | No | cART | cca_0 | 0.850 | 0 | NA | NA |
| 3 | Female | 40 | Urban | Yes | No | cART | cca_12 | 0.925 | 1 | 0.850 | 0.075 |
| 4 | Male | 38 | Urban | No | No | Naive | cca_0 | 0.875 | 0 | NA | NA |
| 4 | Male | 38 | Urban | No | No | Naive | cca_12 | 0.750 | 1 | 0.875 | -0.125 |
| 5 | Female | 49 | Urban | No | Yes | cART | cca_0 | 1.600 | 0 | NA | NA |
| 5 | Female | 49 | Urban | No | Yes | cART | cca_12 | 1.225 | 1 | 1.600 | -0.375 |
And then plot the differences
df2 %>%
na.omit() %>%
ggplot(aes(x = cca_diff)) +
geom_boxplot()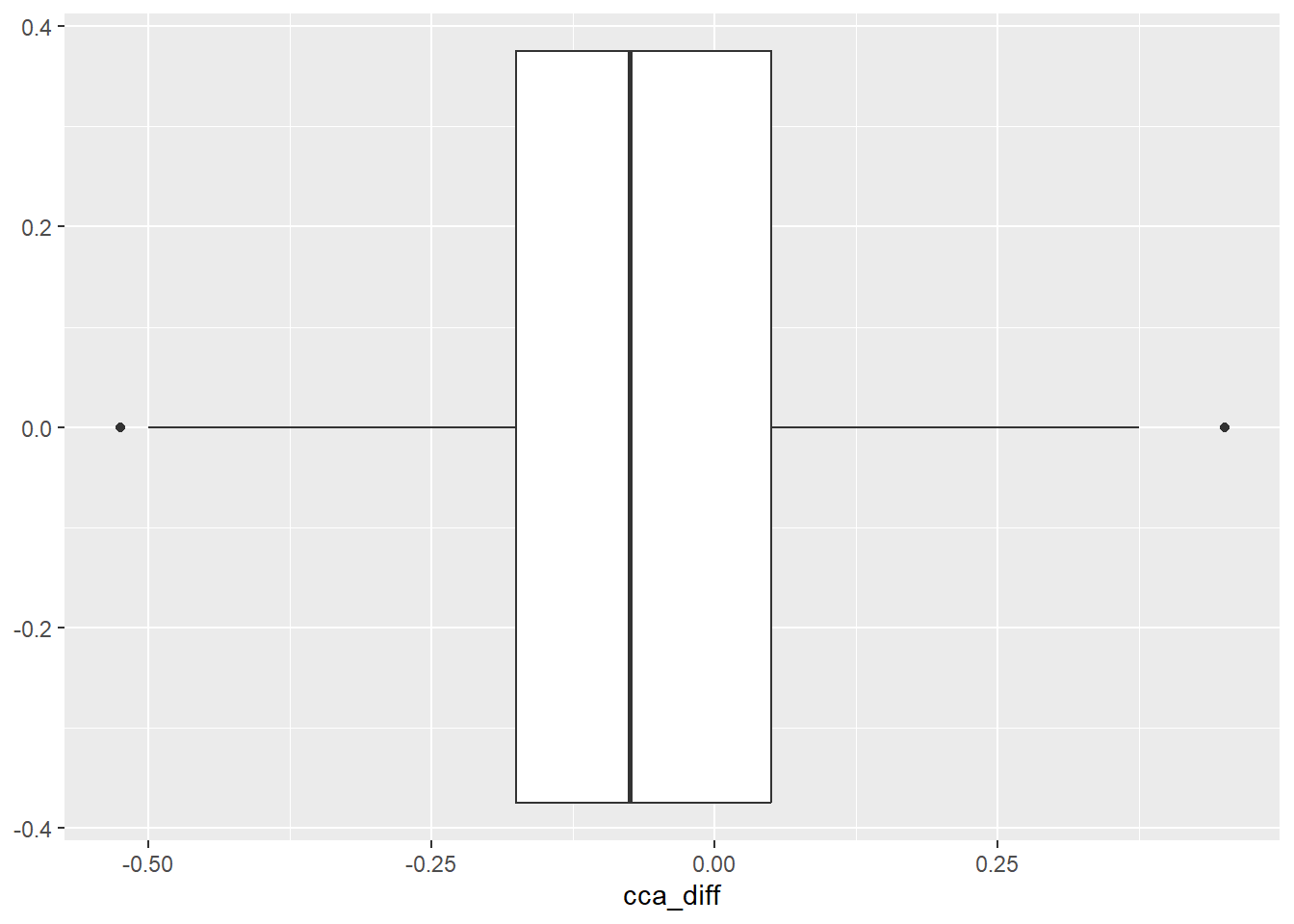
Comment: Generally there was decrease in the cca values over the two time periods. Next we summarise and visualise the data
df %>%
na.omit() %>%
ggplot(aes(x = Time, y = cca, group = sid))+
geom_jitter(show.legend = F, width = .01) +
stat_smooth(
formula = y ~x,
method = "lm",
se = FALSE,
col = "grey") +
theme_light()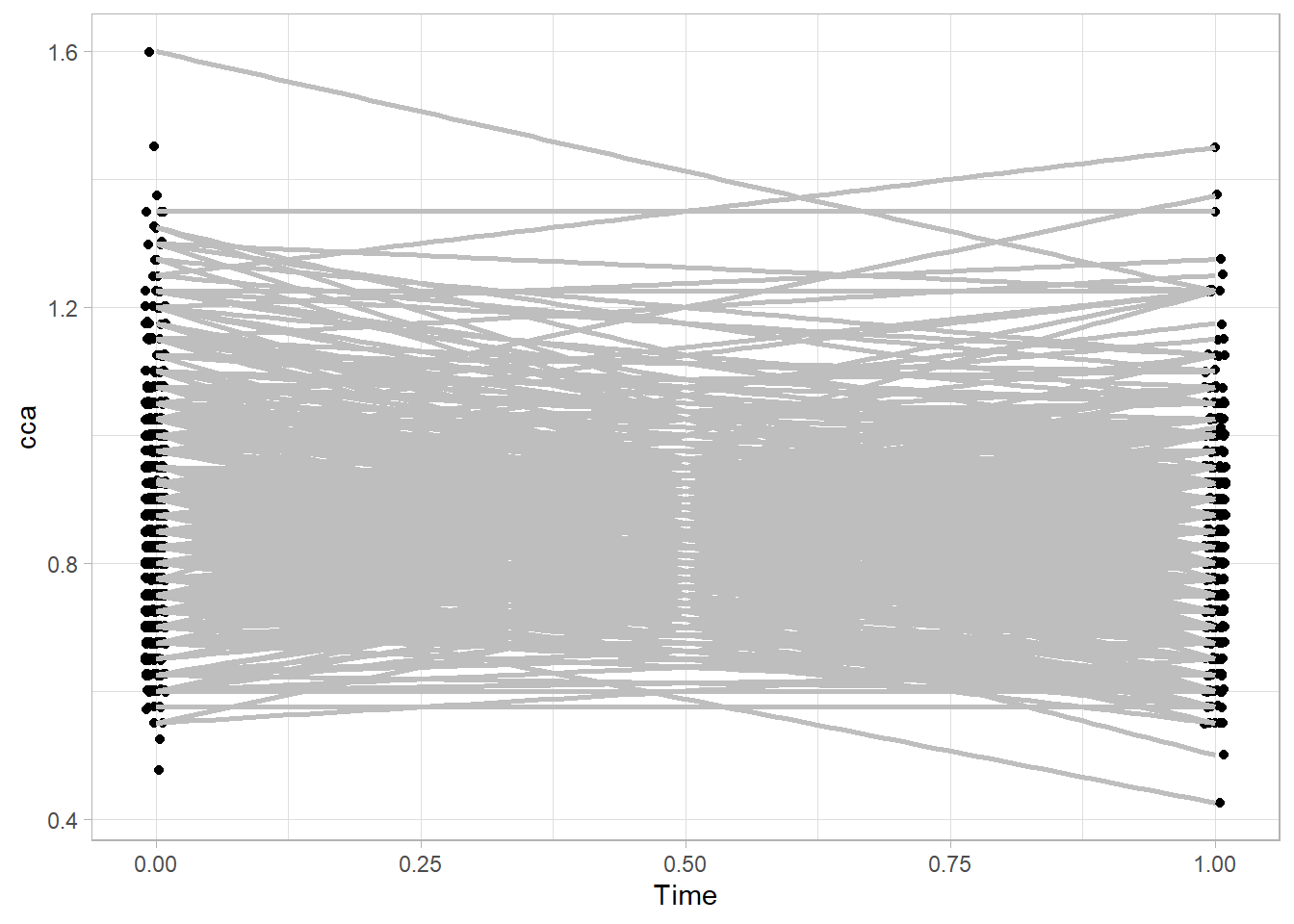
Next the UNCONDITIONAL NULL MODEL to evaluate clustering, thereby finding out if we need to even do multilevel analysis
n0 <-
nlme::gls(
cca ~ 1, data = df, na.action = na.omit, method = "ML")
n0 %>%
broom.mixed::tidy(conf.int=T) %>%
kableExtra::kable()| term | estimate | std.error | statistic | p.value | conf.low | conf.high |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.8520116 | 0.004918 | 173.2448 | 0 | 0.8423726 | 0.8616507 |
n1 <-
nlme::lme(
cca ~ 1, random = ~ 1 | sid,
data = df, na.action = na.omit, method = "ML")
n0 %>% broom.mixed::tidy(conf.int=T) %>% kableExtra::kable()| term | estimate | std.error | statistic | p.value | conf.low | conf.high |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.8520116 | 0.004918 | 173.2448 | 0 | 0.8423726 | 0.8616507 |
n1 %>% reghelper::ICC()[1] 0.3150857anova(n0, n1) Model df AIC BIC logLik Test L.Ratio p-value
n0 1 2 -869.6521 -859.6919 436.8260
n1 2 3 -909.9268 -894.9866 457.9634 1 vs 2 42.27476 <.0001Since ICC > 0.05 and also the random effects CI does not include 0 there exist significant clustering to suggest we do multilevel modeling. Next we test the UNCONDITIONAL SLOPE MODEL using the FIXED slope
n2 <-
nlme::lme(
cca ~ Time, random = ~ 1 | sid,
data = df,
na.action = na.omit,
method = "ML")
n2 %>%
broom.mixed::tidy(conf.int=T) %>%
kableExtra::kable()| effect | group | term | estimate | std.error | df | statistic | p.value | conf.low | conf.high |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fixed | NA | (Intercept) | 0.8629565 | 0.0060113 | 711 | 143.554679 | 0e+00 | 0.8511653 | 0.8747476 |
| fixed | NA | Time | -0.0447315 | 0.0086710 | 362 | -5.158735 | 4e-07 | -0.0617676 | -0.0276955 |
| ran_pars | sid | sd_(Intercept) | 0.0979221 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.0857260 | 0.1118532 |
| ran_pars | Residual | sd_Observation | 0.1268559 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
n2 %>% reghelper::ICC()[1] 0.3733763anova(n0, n1, n2) Model df AIC BIC logLik Test L.Ratio p-value
n0 1 2 -869.6521 -859.6919 436.8260
n1 2 3 -909.9268 -894.9866 457.9634 1 vs 2 42.27476 <.0001
n2 3 4 -932.4301 -912.5098 470.2150 2 vs 3 24.50329 <.0001Next we test the UNCONDITIONAL SLOPE MODEL using the RANDOM slope
n3 <-
nlme::lme(
cca ~ Time,
random = ~ Time | sid,
data = df,
na.action = na.omit,
method = "ML")
n3 %>% summary()Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: df
AIC BIC logLik
-929.0894 -899.2089 470.5447
Random effects:
Formula: ~Time | sid
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.14902004 (Intr)
Time 0.16324990 -0.51
Residual 0.05371762
Fixed effects: cca ~ Time
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 0.8629565 0.005942057 711 145.22857 0
Time -0.0452827 0.008766665 362 -5.16533 0
Correlation:
(Intr)
Time -0.413
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-0.85549105 -0.24307511 -0.02773692 0.23248407 1.46909846
Number of Observations: 1075
Number of Groups: 712 n3 %>% nlme::intervals(which = "fixed")Approximate 95% confidence intervals
Fixed effects:
lower est. upper
(Intercept) 0.85130124 0.86295646 0.87461168
Time -0.06250667 -0.04528273 -0.02805879n3 %>% reghelper::ICC()[1] 0.9442325anova(n0, n1, n2, n3) Model df AIC BIC logLik Test L.Ratio p-value
n0 1 2 -869.6521 -859.6919 436.8260
n1 2 3 -909.9268 -894.9866 457.9634 1 vs 2 42.27476 <.0001
n2 3 4 -932.4301 -912.5098 470.2150 2 vs 3 24.50329 <.0001
n3 4 6 -929.0894 -899.2089 470.5447 3 vs 4 0.65926 0.7192Next we test the FULL MODEL using the RANDOM slope
n4 <-
nlme::lme(
cca ~ Time + hpt_old + sex + scale(ageyrs) + cart,
random = ~ 1 | sid,
data = df,
method = "ML",
na.action = na.omit)
n4 %>%
broom.mixed::tidy() %>%
kableExtra::kable()| effect | group | term | estimate | std.error | df | statistic | p.value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fixed | NA | (Intercept) | 0.8224719 | 0.0101076 | 706 | 81.371922 | 0.0000000 |
| fixed | NA | Time | -0.0650204 | 0.0087880 | 362 | -7.398737 | 0.0000000 |
| fixed | NA | hpt_oldYes | 0.0577155 | 0.0145760 | 706 | 3.959637 | 0.0000827 |
| fixed | NA | sexMale | 0.0290863 | 0.0121127 | 706 | 2.401295 | 0.0165947 |
| fixed | NA | scale(ageyrs) | 0.0280193 | 0.0053049 | 706 | 5.281768 | 0.0000002 |
| fixed | NA | cartcART | 0.0886504 | 0.0119744 | 706 | 7.403327 | 0.0000000 |
| fixed | NA | cartCONTROL | -0.0159617 | 0.0130719 | 706 | -1.221074 | 0.2224656 |
| ran_pars | sid | sd_(Intercept) | 0.0745001 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| ran_pars | Residual | sd_Observation | 0.1259536 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
n4 %>% reghelper::ICC()[1] 0.2591817anova(n0, n1, n2, n3, n4) Model df AIC BIC logLik Test L.Ratio p-value
n0 1 2 -869.6521 -859.6919 436.8260
n1 2 3 -909.9268 -894.9866 457.9634 1 vs 2 42.27476 <.0001
n2 3 4 -932.4301 -912.5098 470.2150 2 vs 3 24.50329 <.0001
n3 4 6 -929.0894 -899.2089 470.5447 3 vs 4 0.65926 0.7192
n4 5 9 -1088.4835 -1043.6628 553.2418 4 vs 5 165.39417 <.0001